Shining a Light on Healing: Low-Level Laser Therapy in Physical Therapy
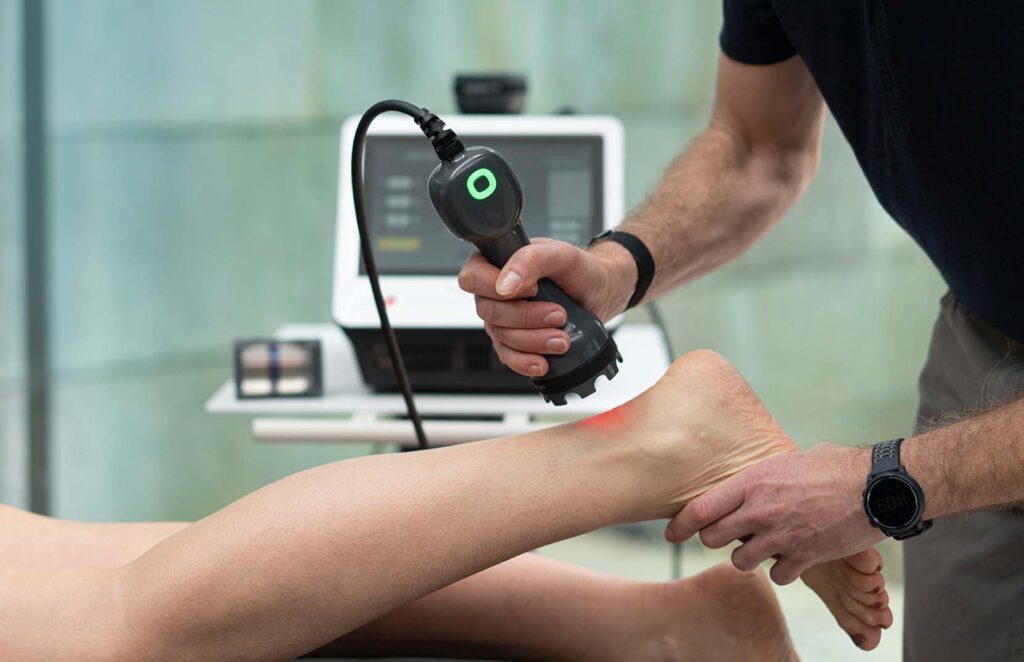
When it comes to innovative approaches to pain relief and accelerated healing, Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) is a shining example. LLLT, often referred to as cold laser therapy, is a non-invasive, painless treatment method that is gaining recognition in the world of physical therapy. In this blog post, we’ll explore what LLLT is, its potential benefits, and the science behind this fascinating technology.
Understanding Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
LLLT is a therapeutic technique that utilizes low-intensity lasers or light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to stimulate healing and reduce pain. These low-level lasers emit non-thermal photons of light that are absorbed by cells. Unlike surgical lasers used for cutting or coagulation, LLLT does not generate heat and is considered safe and painless.
The Apparent Benefits of LLLT in Physical Therapy
- Pain Management: LLLT has shown promise in reducing pain and discomfort associated with various conditions, including musculoskeletal injuries, arthritis, and neuropathy. It is believed to work by blocking pain signals and promoting the release of endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers.
- Accelerated Tissue Repair: LLLT has been reported to enhance the healing process by increasing blood flow to the affected area, promoting cell growth, and reducing inflammation. This makes it valuable for athletes recovering from sports injuries and individuals healing from surgery.
- Improved Range of Motion: By reducing muscle tension and promoting tissue repair, LLLT can enhance flexibility and movement. This is particularly beneficial for patients with conditions like frozen shoulder or stiff joints.
- Non-Invasive and Painless: Unlike some other therapies, LLLT is non-invasive and typically painless. It involves directing the laser or LED light directly to the target area, eliminating the need for incisions or injections.
- Minimal Side Effects: LLLT is considered safe when administered by trained professionals. It has minimal side effects, which may include mild, temporary warmth at the treatment site.
The Science Behind LLLT
The exact mechanisms behind LLLT are still being explored, but it is thought to work by:
- Stimulating Cellular Energy: LLLT is believed to enhance the function of mitochondria, the “powerhouses” of cells, which can lead to improved cell metabolism and tissue repair.
- Increasing Blood Flow: The laser light may trigger the release of nitric oxide, which in turn improves blood flow to the target area, delivering essential nutrients and oxygen.
- Reducing Inflammation: LLLT has been shown to decrease inflammation by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory molecules.
- Nerve Regeneration: Some studies suggest that LLLT may promote nerve regeneration, making it useful for neuropathic conditions.
It’s important to note that LLLT should be administered by trained healthcare professionals who can tailor the treatment to each patient’s unique needs.
In conclusion, Low-Level Laser Therapy is an exciting and non-invasive option in the field of physical therapy, offering relief from pain, improved healing, and enhanced quality of life. As with any medical treatment, consult with a licensed healthcare provider to determine if LLLT is suitable for your specific condition.
Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice on the best treatment options for your individual needs.
Check out Blog posts you may have missed:
Exploring the World of Dry Needling: Benefits and Science Behind It
Finding Relief from Spondylolisthesis: The Role of Physical Therapy